How Do Red Blood Cells Maintain Homeostasis
Homeostasis definition maintaining mechanism flow byju meaning ecosystem negative definitions byjus endocrine external Oxygen erythrocyte levels marrow kidney liver erythropoiesis erythropoietin homeostasis epo cells kidneys controlled anatomy altitude physiology circulatory Cell pathway circulation homeostasis
Frontiers | Red Blood Cell Homeostasis: Mechanisms and Effects of
Homeostasis cellular maintaining maintain Hemostasis blood clotting biology steps process cells vessel secondary flow visionlearning red basic figure components wall Homeostasis of blood glucose (a negative feedback loop)
Feedback loop negative glucose blood homeostasis
Homeostasis maintain cells cell membrane do sodium potassium pump diffusion components ion phospholipid bilayer transport bothHomeostasis lab Homeostasis cells oxygen cycle transport regulate list add experimentsMaintaining homeostasis.
Blood biology iCh103 – chapter 8: homeostasis and cellular function – chemistry How does the cell membrane help cells maintain homeostasisMaintaining homeostasis.

Erythrocyte production is controlled via a negative feedback loop
Cellular apph mechanisms physiology plasticity systems ppt powerpoint presentation sympathetic controlRed blood cells Homeostasis skeletal system maintainingFeedback glucose glucagon homeostasis negative biology loops blood insulin sugar explain positive function role between loop levels pancreas chemistry would.
Homeostasis humansWhat is homeostasis? why is it so important for our wellbeing? Homeostasis physiological adaptation mechanisms maintainsErythrocyte erythrocytes blood destruction marrow physiology anatomy normal 1905 liver circulation breakdown rbcs lifecycle heme macrophages removed haemolysis anaemia destroyed.

Homeostasis: how cells regulate educational resources k12 learning
Homeostasis blood lab glucose liver body cellular libretexts small respiration through will lumen biologyNucleus why Maintain homeostasis cell membrane cells does helpBlood red cell rbc membrane homeostasis mechanisms microvesicle frontiersin disease generation effects health breakdown figure fphys.
File:1905 erythrocyte life cycle.jpgBlood erythrocyte cells red erythrocytes physiology anatomy cell life marrow bone destruction circulation cycle diagram liver deficiency heme recycled into How do cells maintain homeostasisPhysiological homeostasis.


PPT - APPH 6211 Systems Physiology I: Cellular mechanisms of plasticity

How Do Cells Maintain Homeostasis | Biology Dictionary

CH103 – Chapter 8: Homeostasis and Cellular Function – Chemistry
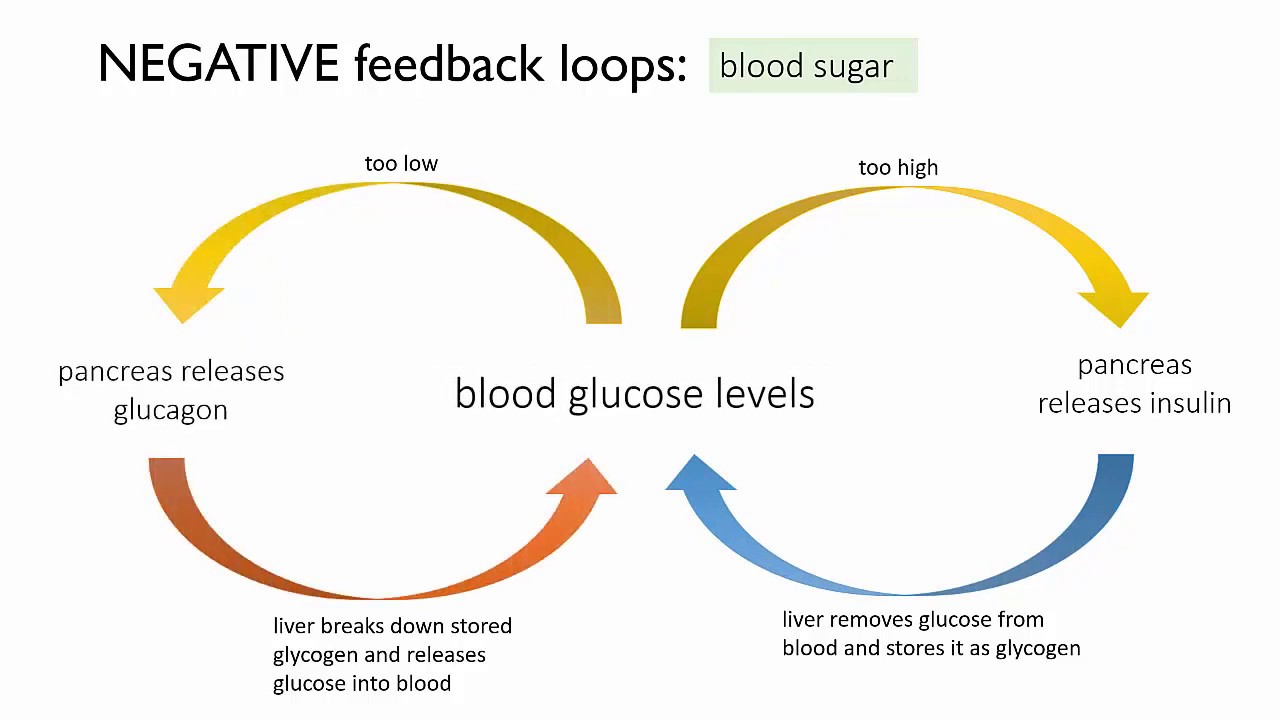
Homeostasis of blood glucose (a negative feedback loop) - YouTube

Red Blood Cells | Absence of a Nucleus - Lesson | Study.com

Frontiers | Red Blood Cell Homeostasis: Mechanisms and Effects of

Maintaining Homeostasis - The Skeletal System

PPT - Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation PowerPoint Presentation

Physiological Homeostasis - Biology Online Tutorial
